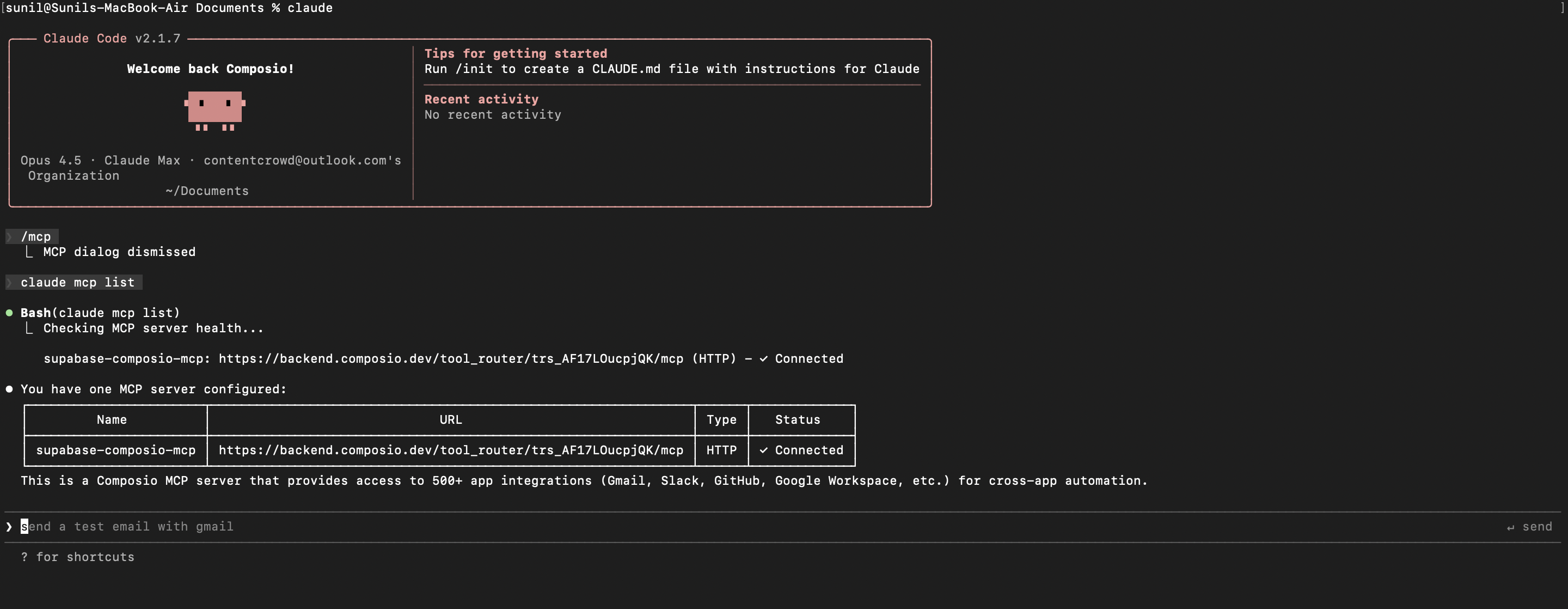
Ignisign API AuthenticationTool to authenticate an application over Ignisign API and retrieve a JWT.
Cancel Signature RequestTool to cancel a signature request.
Initialize DocumentTool to initialize a document for a signature request.
Create SignerTool to create a new signer.
Create Webhook EndpointTool to create a new webhook endpoint for an application.
Delete DocumentTool to delete a specific document by its ID.
Delete Ignisign Signature RequestTool to delete a signature request.
Delete SignerTool to delete a signer.
Delete Webhook EndpointTool to delete a specific webhook endpoint.
Get application contextTool to retrieve the global context of an application.
Get Document InformationTool to retrieve document metadata by ID.
Get Missing Signer InputsTool to determine missing inputs needed for a signer in a specific signature profile.
Get Signature Request DetailsTool to retrieve detailed information for a specific signature request.
Get Signature Request DocumentTool to retrieve the document associated with a specific signature request.
Get Signature RequestsTool to retrieve a paginated list of signature requests for an application.
Get Signature Request StatusTool to retrieve the current status of a specific signature request.
Get Signed DocumentTool to download the signed document (signature proof) for a signature request.
Get Signer Creation ConstraintsTool to retrieve input constraints required to create a signer for a specific signature profile.
Get Signer Input ConstraintsTool to get signer input constraints.
Get Signer InputsTool to retrieve inputs provided by a signer for a signature request.
Get Signer ProfileTool to retrieve a signer profile.
Get Signer ProfilesTool to retrieve signer profiles.
Get Webhook DetailsTool to retrieve details of a specific webhook endpoint.
Get WebhooksTool to list all webhook endpoints configured for an application environment.
Close Ignisign Signature RequestTool to close an active signature request.
Update SignerTool to update details of an existing signer.
Initialize Ignisign Signature RequestTool to initialize a new signature request.
List DocumentsTool to retrieve documents linked to a signature request.
Provide Document Content Data JSONTool to provide JSON content for a document.
Provide Document Content FileTool to provide file content for a document.
Provide Document Content Private FileTool to provide private content for a document via its SHA-256 hash.
Publish Signature RequestTool to publish a draft signature request.
Search SignersTool to search for signers within an application.
Update Document InformationTool to update document metadata.
Update Signature RequestTool to partially update a signature request in DRAFT state.
Update Webhook EndpointTool to update an existing webhook endpoint.