AI search engines are everywhere right now, and 2026 is shaping up to be the year they fully change how we search.
Search has moved past simple keywords and long lists of links. AI-powered search engines try to understand what you mean and return clear answers about what is happening right now. As more of these platforms appear, it gets harder to know which ones actually deliver on those promises.
That is where the real challenge comes in. When everything sounds powerful, choosing the right tool becomes confusing.
So the real question is this: which tools give you fresh, accurate answers, help you move faster, and are truly ready for real-world use in 2026?
This article looks at the leading options in AI search today and how well they live up to those claims.

What Makes a Good AI Search Tool in 2026
A good AI search tool in 2026 should feel simple. You ask something, it understands you, and you get a useful answer fast.
It starts with fresh results. A strong tool pulls in new information quickly and keeps answers updated as things change. When results fall behind, the whole experience feels unreliable.
Next comes understanding. You should be able to ask questions naturally, without thinking about perfect wording. The tool needs to catch what you really mean, even if your question is short or casual.
Then there is the answer itself. It should be clear, easy to read, and ready to use without extra work. Speed ties it all together. Long waits break the flow, so search should feel quick and consistent, even when the question is complex.
And finally, there is trust. You should know where the answers come from and have control over what happens to your data.
Categories of AI Search Tools
Before looking at specific tools, it helps to understand the main types of AI search that exist today.
Not every AI search engine is built for the same purpose. Some are made for everyday users, some for developers, and some for heavy data work.
These are the main categories you will see in 2026.
Consumer AI Search Engines: Built for normal users who want quick answers, summaries, and explanations.
Developer-Focused Search APIs: Made for apps, agents, and products that need search built in.
Crawling and Data Extraction Tools: Used to collect, clean, and structure data from websites.
Research and Knowledge Tools: Focused on deep research, long answers, and citations.
Enterprise Search Platforms: Designed for teams that need search across internal documents, files, and systems.
AI Search Tools Compared
Here is a quick side-by-side comparison of the most popular AI search tools in 2026, highlighting their purposes, features, and who they are best suited for.
Tool | Best For | Live Web Access | Answer Style | Developer / API-First | Privacy Focus | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Exa | AI builders, agents, RAG systems | Yes | Structured, intent-based | Yes | Medium | Medium |
Tavily | AI agents & workflows | Yes | API-ready, structured | Yes | Medium | Medium |
Firecrawl | Web data crawling & extraction | Yes (via crawl) | Raw structured data | Yes | Low | Medium |
Perplexity | Everyday search & research | Yes | Chat & concise with sources | Limited | Medium | High |
You.com | Privacy-aware users | Yes | Mixed (chat + links) | Limited | High | High |
Serp Tools | Developers needing raw results | Yes | Raw search results | Yes | Depends on setup | Medium |
Brave Search API | Privacy-centric products | Yes | Search output only | Yes | High | Medium |
Phind | Developers & coders | Yes | Code-oriented, explainer style | Limited | Medium | High |
Andi | Visual, everyday users | Yes | Card-style summaries | No | High | High |
Parallel AI Search | Agents, research systems, complex queries | Yes | Aggregated from parallel searches | Yes | Medium | Medium |
Best AI Search Engine Tools for 2026
Here are the AI search tools that are setting the standard in 2026, each solving search in a different way depending on who it is built for.
1. Exa
Exa is an AI-first search engine built around meaning, not keywords. It uses neural search and embeddings to understand what a query is really asking and then finds content that matches intent, not just popular pages.
Rather than acting like a traditional search engine with ads and ranking tricks, Exa is designed to be a search layer for AI systems. It is widely used inside agents, research tools, and AI products that need high-quality, up-to-date web data.
Exa works mainly through an API. Teams plug it into agents, workflows, or internal tools that need live web search. It supports semantic search, similarity search, domain-restricted search, and structured outputs with citations. This makes it useful for building tools that need reliable sources rather than noisy results.
A big focus of Exa is quality. It tries to avoid spam and low-value pages, aiming to return content that is actually useful.
Who Exa is for: Exa is best for developers, AI builders, and teams that need smart web search inside their products or agent workflows.
Core strengths of Exa
Semantic-first search: Focuses on meaning and intent, not keyword matching.
Strong on complex queries: Handles long, vague, or multi-part questions well.
Built for AI workflows: Designed to plug into agents, RAG systems, and LLM apps.
Higher-quality sources: Filters out a lot of spam and SEO-heavy pages.
Flexible search modes: Supports similarity search, domain filtering, and structured outputs.
Pros
High-quality results: Consistently returns more useful pages than basic scraping or generic search APIs.
Great for AI systems: Works smoothly with agents, RAG pipelines, and LLM-based tools.
Developer-friendly: Clean API, good docs, and easy integration.
Cons
Not user-focused: UI is basic and not meant for casual browsing.
Technical setup needed: Best features require developer work.
Cost at scale: Can become expensive with heavy or enterprise usage.
2. Tavily
Tavily is an AI-focused search tool built mainly for agents and automated workflows. It is designed to give AI systems fast, clean, and structured search results that can be used directly inside reasoning or action-taking pipelines.
Unlike consumer search engines, Tavily is not trying to be a browsing experience. Its main goal is to act as a reliable search layer for AI agents that need fresh web data to think, plan, and act.
Tavily works through an API and is commonly used in agent frameworks, tool-using LLMs, and workflow automation systems. It focuses on speed, simplicity, and consistency rather than fancy interfaces. It supports web search, result summarization, structured outputs, and filtering, making it easy for agents to pull in information and use it without extra cleaning.
Who Tavily is for: Tavily is best for developers and teams building AI agents, automation systems, and tool-using LLM workflows.
Core strengths of Tavily
Agent-first design: Built specifically for AI agents and tool-using models.
Fast search layer: Optimized for quick responses inside agent loops.
Structured outputs: Results are easy for machines to read and use.
Simple integration: Clean API with minimal setup.
Good for planning tasks: Works well when agents need to search, think, and act.
Pros
Great for agent workflows: Fits naturally into multi-step reasoning systems.
Fast and reliable: Low latency for repeated calls.
Easy to use: Simple API and quick setup.
Cons
Not for normal users: No consumer-friendly interface.
Limited browsing features: Focused on function, not exploration.
Depends on external sources: Quality depends on what it can access.
3. Firecrawl
Firecrawl is a crawling and data-extraction tool designed to turn messy websites into clean, usable data. Instead of acting like a search engine for humans, it focuses on helping machines collect, structure, and understand web content.
It is mainly used when you need to pull data from many pages, clean it up, and feed it into AI systems, databases, or internal tools. Firecrawl handles crawling, parsing, and formatting so teams do not have to build their own scrapers.
Firecrawl works through an API and supports crawling single pages, full websites, or large URL lists. It can return data in formats that are easy for AI models and pipelines to consume. It is commonly used in RAG systems, data pipelines, research tools, and internal search systems where raw web data needs to be cleaned before use.
Who Firecrawl is for: Firecrawl is best for developers and teams that need to collect, clean, and structure web data for AI, analytics, or internal systems.
Core strengths of Firecrawl
Website crawling: Can crawl single pages or entire sites at scale.
Clean extraction: Turns messy HTML into structured, usable data.
AI-friendly output: Formats data so it works well with LLMs and pipelines.
API-first design: Easy to plug into workflows and tools.
Scales well: Handles large crawling jobs reliably.
Pros
Saves time: No need to build and maintain your own scrapers.
Good for RAG: Clean data works well for AI knowledge systems.
Flexible usage: Works for small and large crawling jobs.
Cons
Not a search engine: You need to know what to crawl.
Requires setup: Needs planning for large-scale crawls.
Can get expensive: Heavy crawling increases costs.
Parallel AI Search is built for speed and scale. It focuses on running many searches at the same time and combining the results into a single, clean answer. Instead of doing one search step by step, it breaks a query into parts, searches in parallel, and merges everything back together.
This makes it useful for complex questions that need information from many places at once. It is often used in agent systems and research tools where one question turns into many sub-questions.
Parallel AI Search is mostly used through APIs and agent frameworks. It fits well in workflows where an AI needs to explore multiple angles of a problem quickly.
The main idea is simple: faster answers by searching in parallel instead of in sequence.
Who Parallel AI Search is for: Parallel AI Search is best for developers and teams building agents, research systems, or tools that need to explore many sources at the same time.
Core strengths of Parallel AI Search
Parallel querying: Runs many searches at once instead of one by one.
Good for complex questions: Works well when one query needs many sub-queries.
Agent-friendly: Designed to plug into agent and tool-using workflows.
Fast aggregation: Combines results into a single response quickly.
API-first design: Built mainly for programmatic use.
Pros
Very fast for big questions: Parallel search saves time.
Good for agents: Fits multi-step reasoning systems well.
Scales well: Handles many queries at once.
Cons
Not for casual users: No simple consumer interface.
Needs setup: Best used with technical workflows.
Quality depends on sources: Output depends on what it searches.
5. Perplexity
Perplexity is a conversational AI search engine built for people who want direct answers, not pages of links. You ask a question, and it responds with a clear answer, usually backed by visible sources.
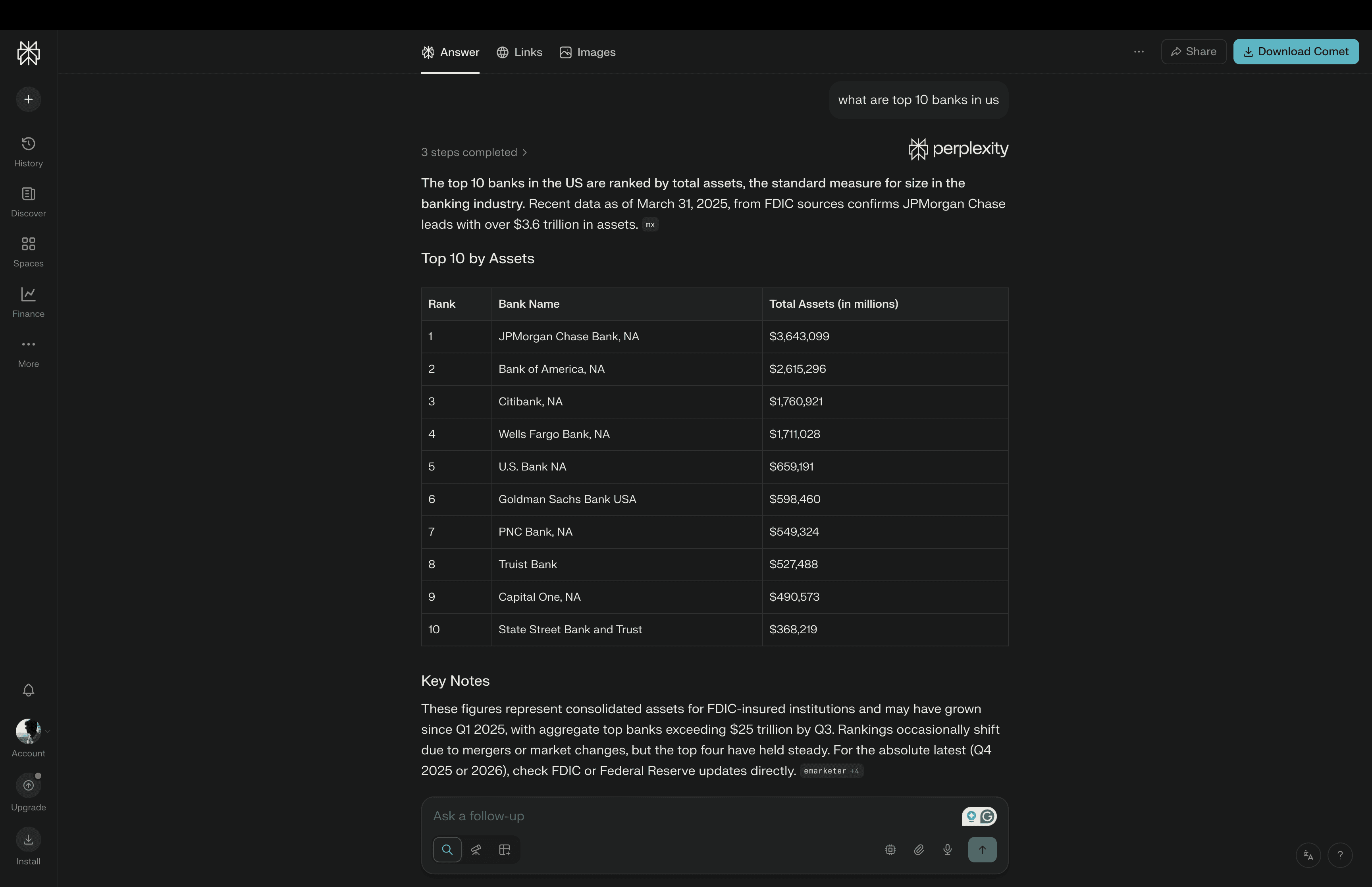
It works like a chat-first search engine. You can ask follow-up questions, go deeper into a topic, or change direction without starting over.
One of Perplexity’s biggest strengths is how it mixes live web search with AI reasoning. It pulls in recent information and turns it into short, readable explanations.
Perplexity also offers different modes, including general search, academic-style research, and focused browsing. Some versions support file uploads and long-context analysis, which makes it useful for working with documents too. It is widely used for learning, writing, research, news tracking, and quick fact-checking.
Who Perplexity is for: Perplexity is best for everyday users, students, writers, researchers, and professionals who want fast answers with clear sources.
Core strengths of Perplexity
Conversational search: Ask naturally and keep the conversation going.
Strong citations: Most answers come with visible sources.
Real-time info: Pulls in recent content from the web.
Multiple modes: Supports general, research, and focused search styles.
Document support: Can work with uploaded files in some plans.
Pros
Very easy to use: No setup, works right away.
Good for learning and writing: Explains topics clearly.
Builds trust: Sources are easy to check.
Cons
Limited control: Not made for deep customization.
Not developer-first: APIs and automation are limited.
Answer depth varies: Some topics get shallow coverage.
6. You search
You search is an AI-powered search engine that focuses on giving users more control over how search works. Instead of a fixed layout, it lets you customize what you see and how results are shown.
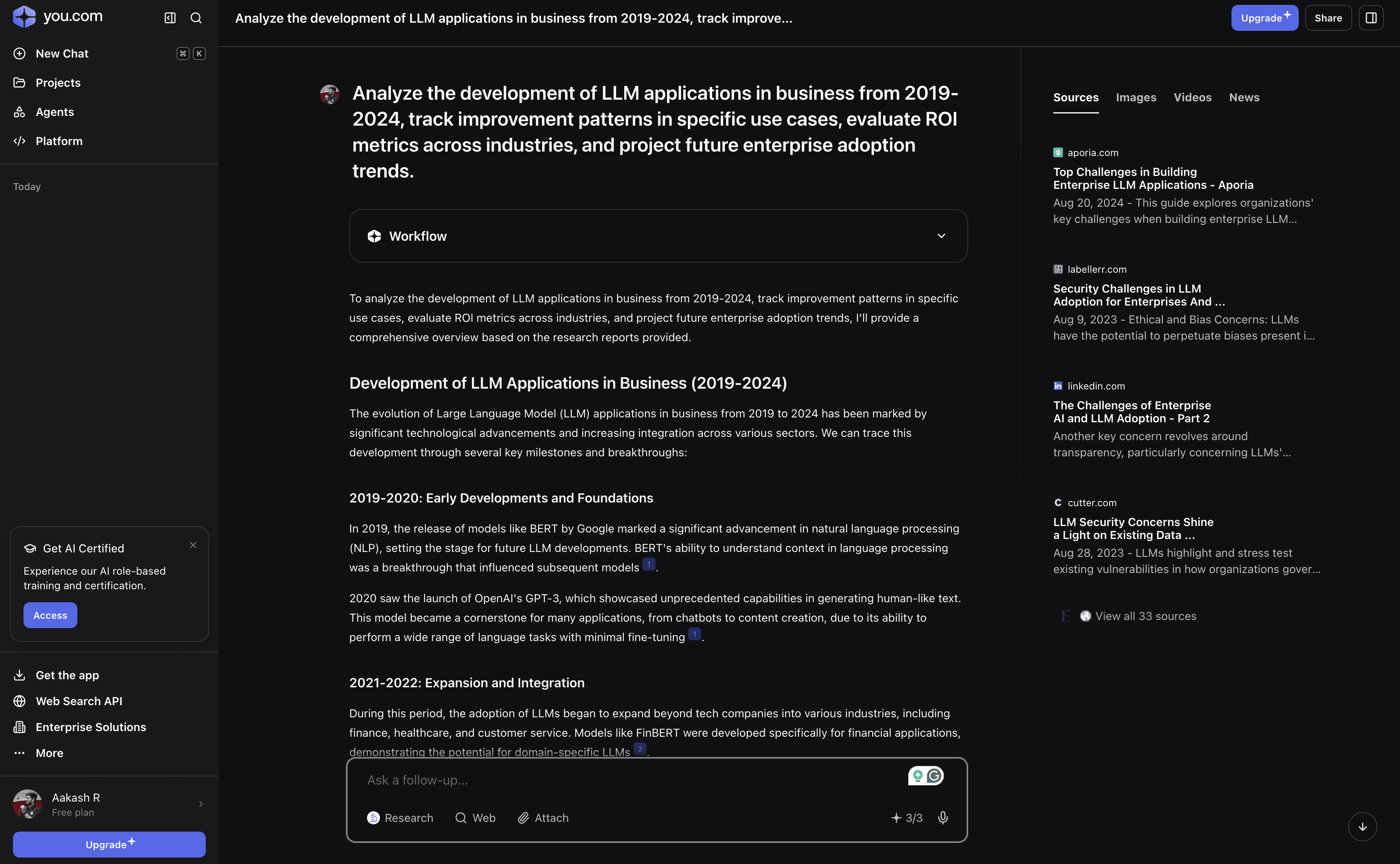
It combines AI answers with regular web results. You can get summaries, chat-style responses, and links on the same page. A big part of You.com is privacy. It avoids heavy tracking and does not depend as much on targeted ads. It also offers different “apps” or modes inside search, such as coding help, writing, research, and general chat, all in one place.
Who You.com is for: You.com is best for users who want a customizable, privacy-focused AI search experience.
Core strengths of You search
Customizable layout: Users can choose how results are displayed.
AI plus web results: Mixes chat answers with links.
Privacy focus: Less tracking and fewer ads.
Multiple apps: Writing, coding, research, and chat in one place.
Good for daily use: Works well as a main search engine.
Pros
User control: You decide how search looks and feels.
Privacy-friendly: Less data tracking than big engines.
Versatile: Useful for many everyday tasks.
Cons
AI quality varies: Some answers are weaker than top AI models.
Can feel busy: Too many options for some users.
Less developer focus: Not built mainly for APIs or automation.
7. Serp (SerpAPI and similar tools)
Serp tools are not search engines for humans. They are tools that let developers pull search results from major search engines in a clean, structured way. Instead of scraping pages yourself, you send a query to a Serp API and get back organized data like links, titles, snippets, images, news, and more.
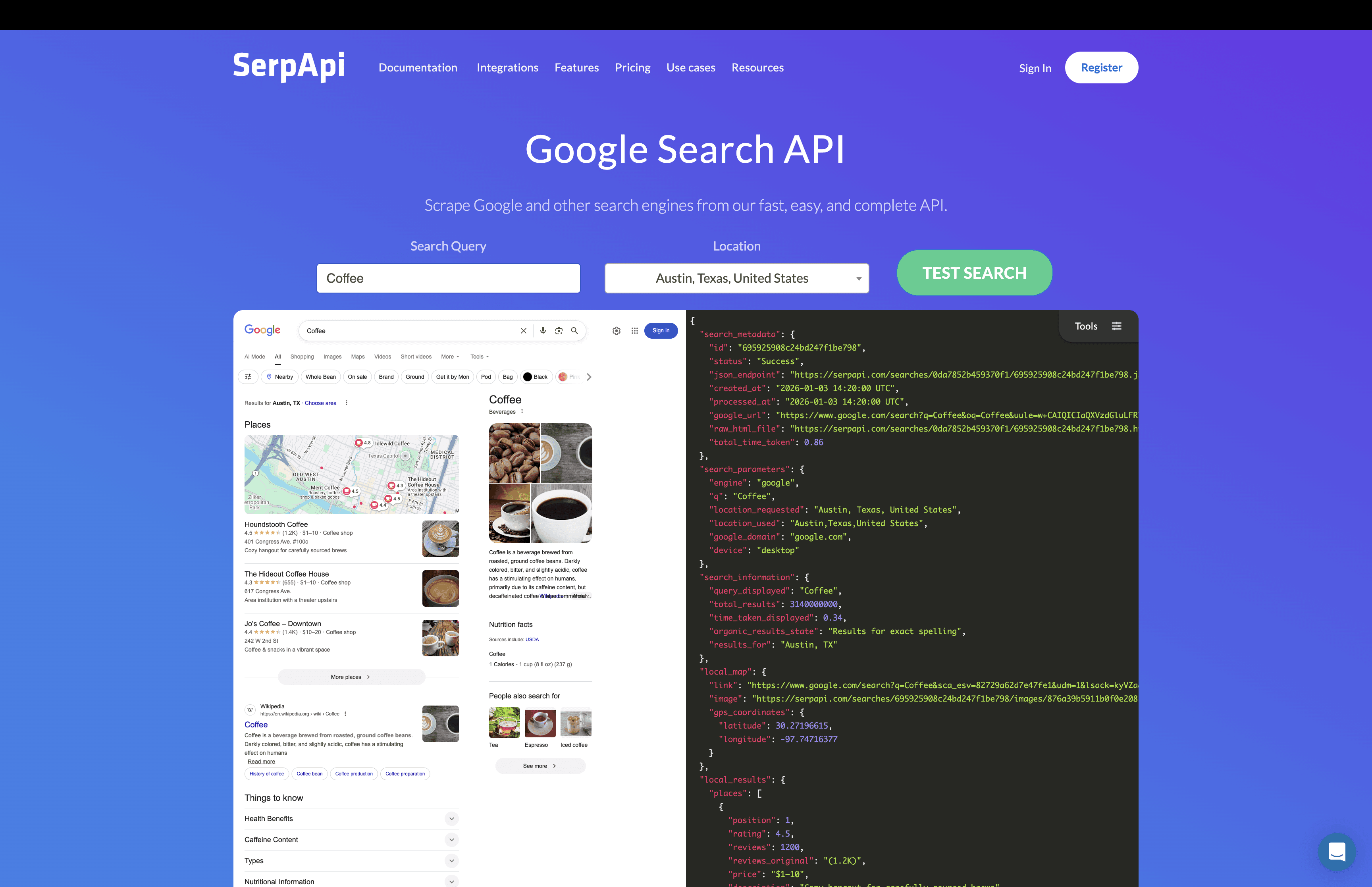
These tools are widely used in analytics, SEO tools, market research, monitoring systems, and AI products that need access to real search results. Serp tools focus on reliability. They handle proxies, captchas, rate limits, and formatting so teams do not have to build and maintain their own scraping systems.
Who Serp is for: Serp tools are best for developers, data teams, and businesses that need large-scale access to search engine results.
Core strengths of Serp tools
Real search engine data: Pulls results from major engines in real time.
Structured output: Returns clean JSON instead of messy HTML.
Scales well: Built for high-volume requests.
Handles scraping issues: Manages proxies, blocks, and captchas.
Good for monitoring: Useful for tracking rankings, trends, and changes.
Pros
Reliable access: No need to build your own scraper.
Works at scale: Handles large workloads smoothly.
Flexible use: Fits analytics, SEO, research, and AI products.
Cons
Not an AI search engine: Just gives raw results, not answers.
Needs processing: You must clean or summarize results yourself.
Can be expensive: High usage increases cost.
8. Brave Search API
Brave Search API is built on Brave’s own independent search index. Unlike many tools that rely on other big search engines, Brave runs its own crawler and index, which gives it more control over data quality and privacy.
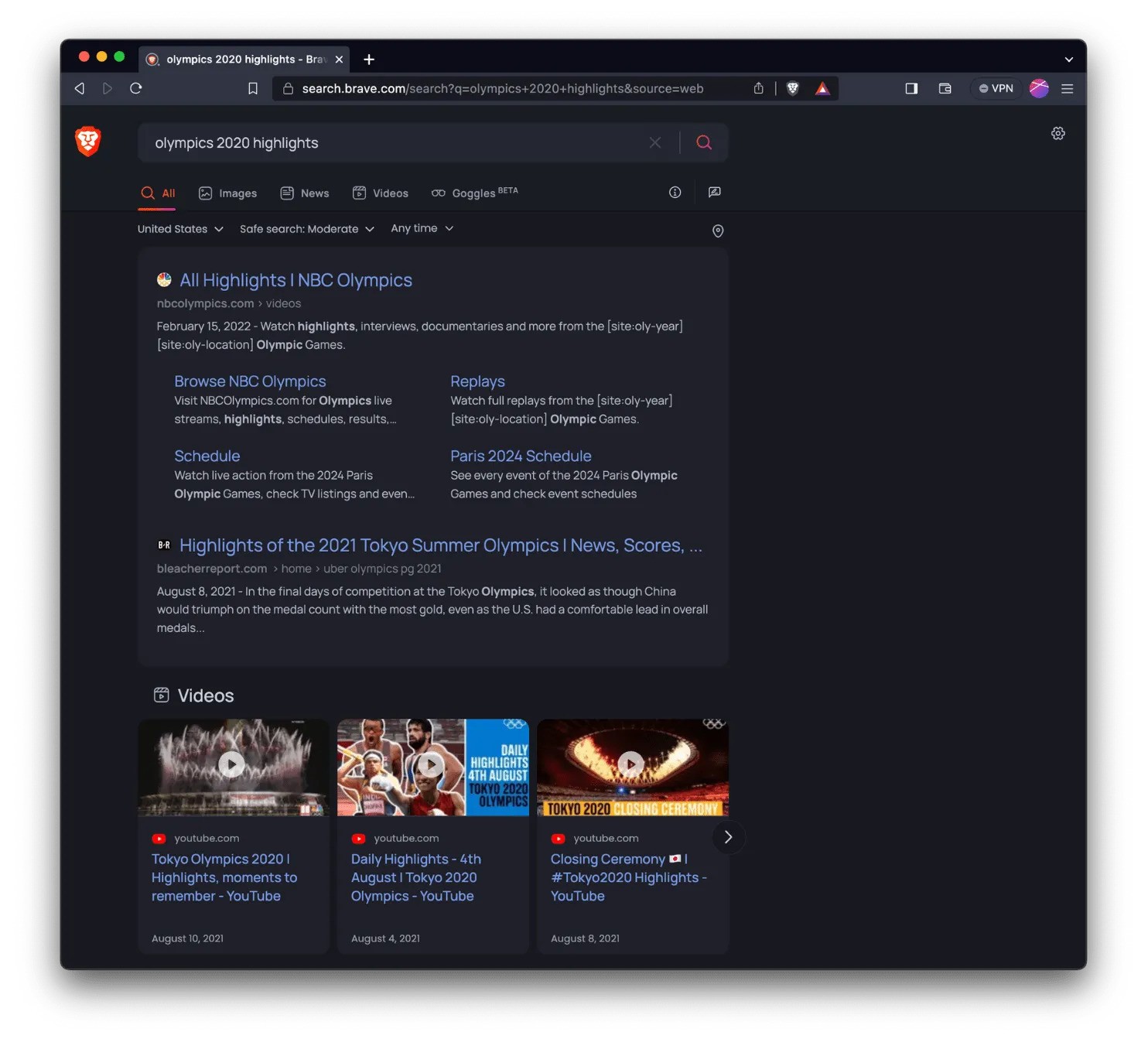
The API is mainly used by developers who want real web search results without relying on Google or Bing. It is often used in AI apps, agents, browsers, and privacy-focused products.
Brave Search also supports AI-style answers on top of its index, but its biggest value is giving clean, direct access to raw search data.
Who Brave Search API is for: Brave Search API is best for developers and teams that want an independent, privacy-friendly web search inside their products.
Core strengths of the Brave Search API
Independent index: Does not depend fully on other search engines.
Privacy-first design: Minimal tracking and data collection.
Good for AI apps: Works well as a search layer for agents and LLM tools.
Structured results: Easy to process programmatically.
Reliable crawling: Continuously updates its own index.
Pros
More control: Not tied to Google or Bing rules.
Privacy-friendly: Strong focus on user data protection.
Good for AI use: Fits well into agent and RAG systems.
Cons
Smaller index: Not as large as big search engines.
Answer quality varies: Depends on index coverage.
Developer-focused: Not built for casual users.
9.Andi Search
Andi is an AI search engine built around a clean, visual, and privacy-first experience. It focuses on presenting answers in a card-style layout with images, links, and short explanations, rather than long text blocks.
It is designed for people who like to explore topics visually. Search results often include summaries, media, and key points arranged in an easy-to-scan format. Andi also puts strong emphasis on privacy. It avoids heavy tracking and keeps the search simple and lightweight.
It works well for general browsing, learning, and discovery, especially when you want a more visual way to explore information.
Who Andi is for: Andi is best for everyday users who want a clean, visual, and privacy-friendly search experience.
Core strengths of Andi
Visual layout: Results appear as cards with text, links, and images.
Privacy-first: Minimal tracking and data collection.
Easy to explore: Good for browsing and discovery.
Simple interface: Clean and uncluttered design.
AI summaries: Short explanations instead of long pages.
Pros
Very clean UI: Easy on the eyes and simple to use.
Good for exploration: Nice for learning and browsing.
Privacy-friendly: Strong stance on user data.
Cons
Not for deep research: Limited control over results.
No strong developer focus: Not built for APIs or automation.
Answer depth varies: Some topics stay surface-level.
How to Choose the Right AI Search Tool
Picking the right AI search tool depends on what you actually want to do with it. Here are the main things to think about.
Start with your goal: Decide whether you need search for everyday use, learning, research, or building products and agents.
Check how fresh the data is: If you care about news, trends, or fast-changing topics, make sure the tool pulls live or near-real-time information.
Think about control: Some tools are simple and hands-off, while others let you filter sources, tune results, and shape how search works.
Look at privacy: See what data is collected, how long it is stored, and whether you can opt out of tracking.
Plan for cost and scale: A tool that is cheap for light use can get expensive at high volume, so check pricing early.
Closing
AI search in 2026 is about more than finding links. It focuses on giving clear answers, staying current, and saving time.
Some tools are built for everyday users who want quick answers. Others are made for developers, agents, and teams building products. There is no single best option for everyone.
The right choice depends on how you work, what you search for, and how much control you want. Once you are clear on that, picking the right AI search tool becomes much easier.
The tools in this list show where search is heading, and they give a good picture of what modern search looks like in 2026.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes an AI search engine different from traditional search engines?
AI search engines focus on understanding intent and meaning instead of just matching keywords. Instead of returning a long list of links ranked by ads or SEO tactics, they aim to deliver direct answers, cleaner sources, or structured data. Many are designed to work inside AI systems, agents, or research workflows rather than for casual browsing.
Are these tools meant for regular users or mainly for developers?
It depends on the tool. Products like Perplexity, You.com, and Andi are built for everyday users who want fast answers and easy exploration. Tools like Exa, Tavily, Firecrawl, Serp APIs, and Brave Search API are designed mainly for developers and teams that need search inside AI products, agents, or data pipelines.
Which AI search tool is best for building AI agents or RAG systems?
For agent and RAG workflows, tools like Exa, Tavily, Firecrawl, Parallel AI Search, and Brave Search API are usually the best fit. They offer APIs, structured outputs, and more control over sources, which is important when search results are fed directly into AI models.
Do AI search tools replace Google completely?
Not entirely. AI search tools often replace Google for learning, research, and quick answers. For developers and teams, they can replace scraping or manual search inside products. Traditional search engines still matter for broad discovery and very large indexes, so many people and systems end up using both.